Watch for fireballs across sky this week as two meteor showers expected to peak
Published 9:14 am Monday, October 7, 2019
Fireballs may flash across night sky as 2 meteor showers peak this week
By Accuweather
Two meteor showers will peak on consecutive nights this week, including one known for bringing incredibly bright meteors known as fireballs.
The back-to-back meteor showers will give stargazers of all ages several chances to spot some shooting stars right from their backyard.
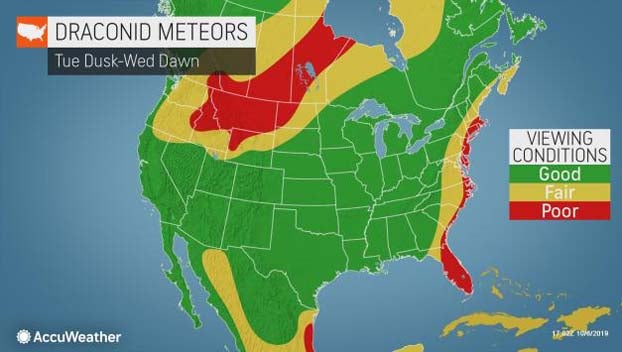
Draconid meteor shower
When: Tuesday, Oct. 8 into Wednesday, Oct. 9
October features the peak of three meteor showers, with the first reaching its climax on Tuesday evening.
“The Draconids meteor shower kicks off the fall meteor shower season,” Dave Samuhel, AccuWeather astronomy blogger and meteorologist, said.
The Draconids are considered a minor meteor shower with only around 10 meteors per hour but, on occasion, can fill the sky with hundreds of meteors. One such outburst happened in 2018 when observers in Europe counted over 140 meteors per hour, according to the International Meteor Organization.
An outburst like this is not expected in 2019. However, the Draconids are notorious for being unpredictable, so there is still a chance for a burst for an hour or two with much higher rates, Samuhel said.
Unlike most meteor showers that are best viewed during the second half of the night, the Draconids come in greatest numbers before midnight.
“This is a good shower for younger stargazers, especially since the shower peaks on a school night,” Samuhel said.
Unfortunately, the moon will be in the sky during this part of the night, so stargazers should look for meteors in areas of the sky away from the bright moon.
Mainly cloud-free conditions are in the forecast across much of the United States on Tuesday night for the Drocinids, but clouds could hinder views for stargazers in the Southeast, northern Plains and perhaps part of the Northeast coast.
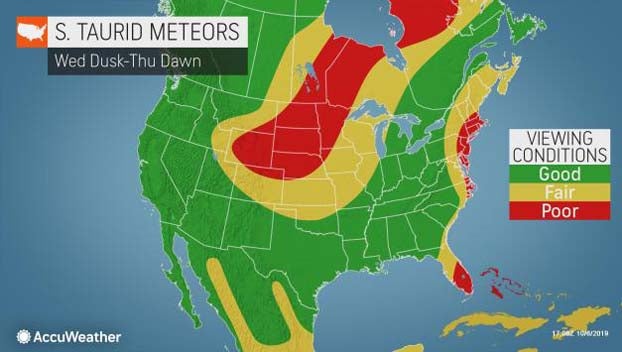
Southern Taurid meteor shower
When: Wednesday, Oct. 9 into Thursday, Oct 10
Immediately following the Draconids will be the Southern Taurids, the second meteor shower to peak in as many nights.
Similar to the Draconids, the Southern Taurids are a minor shower with fewer than 10 meteors per hour, but don’t let the slim numbers discourage you.
“The Taurids are rich in fireballs,” the American Meteor Society said on their website.
Fireballs are meteors that appear incredibly bright as they streak through the sky. They can be so bright that they can cast shadows on the ground for several seconds.
Mainly clear skies will allow for uninterrupted viewing conditions for much of the U.S. on Wednesday night with the exception of widespread clouds over the northern Plains, as well as along the coastal Northeast.
Folks that miss these meteor showers do not have to wait long for another opportunity to spot some shooting stars. The Orionid meteor shower peaks later this month on the night of Oct. 21 into Oct. 22 and usually brings around 20 meteors per hour.
Where to look in the sky during a meteor shower
One of the biggest misconceptions with meteor showers is that you need to look in a certain part of the sky to see shooting stars, when the opposite is true.
During the peak of a meteor shower, meteors are visible in all areas of the sky, not just near the radiant point.
“You want to get as much sky in your field of view as possible,” Samuhel said. “My favorite approach to meteor viewing is to find a conformable lounge chair or even just a yoga mat to lie on.“
Although you do not need to look at the radiant point, its location in the sky is still important. The higher the radiant point is in the sky, the greater number of meteors will be visible.
Knowing where the radiant point of the Dracondis and the Southern Taurids will also help onlookers know the origin of meteor they have seen. If you see a shooting star and trace it backward, it will point toward the shower’s radiant point.
Onlookers that see meteors originating from the northwestern sky will know that they are part of the Draconids.
Meanwhile, those that can be traced back to the eastern sky will be part of the Southern Taurids.
More News